本文最后更新于:2025年4月17日 晚上
画线算法
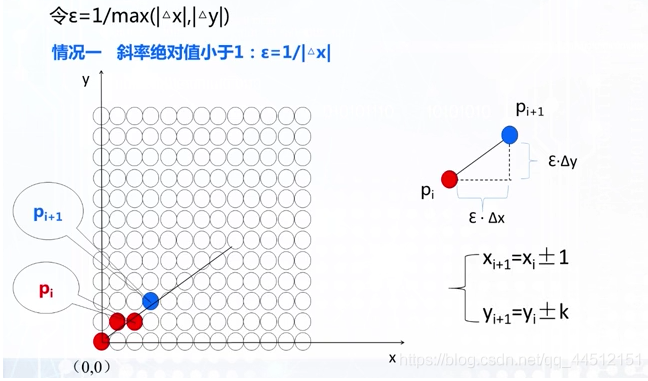
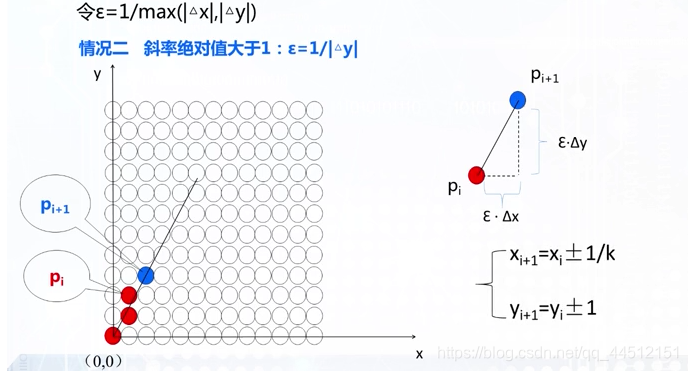
DDA画线
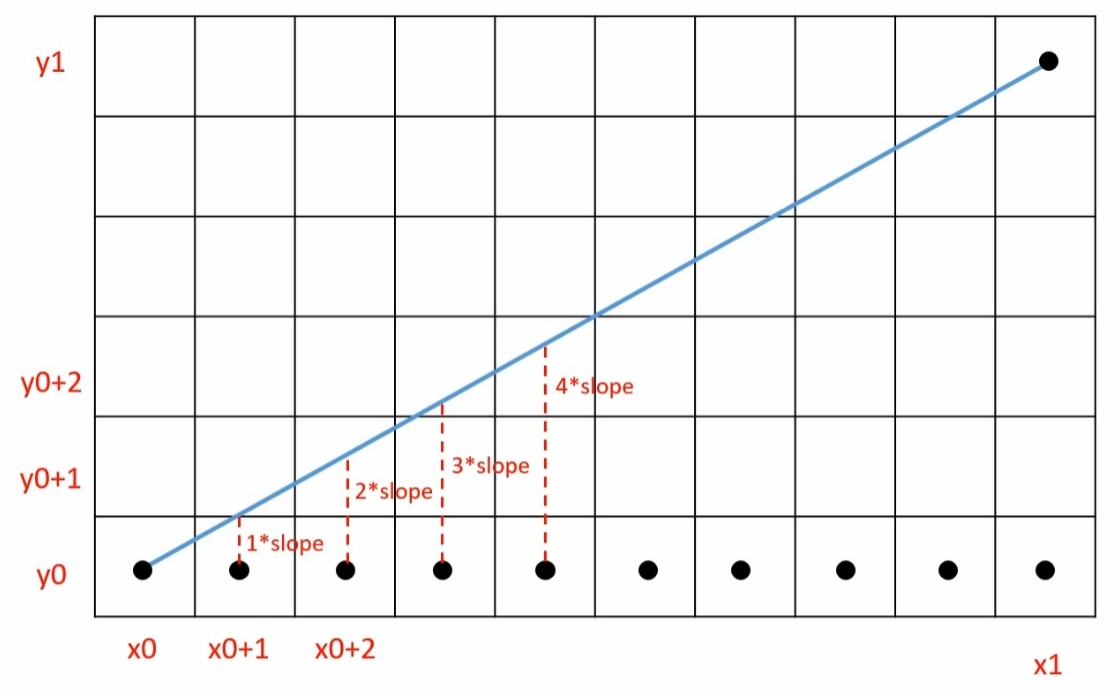
直线方程表示为 y = k x + b y = kx + b y = k x + b
当 ∥ k ∥ < = 1 \lVert k \rVert <= 1 ∥ k ∥ <= 1 x x x 1 1 1 y y y k k k
当 ∥ k ∥ ≥ 1 \lVert k \rVert \geq 1 ∥ k ∥ ≥ 1 x x x 1 / k 1/k 1/ k y y y 1 1 1
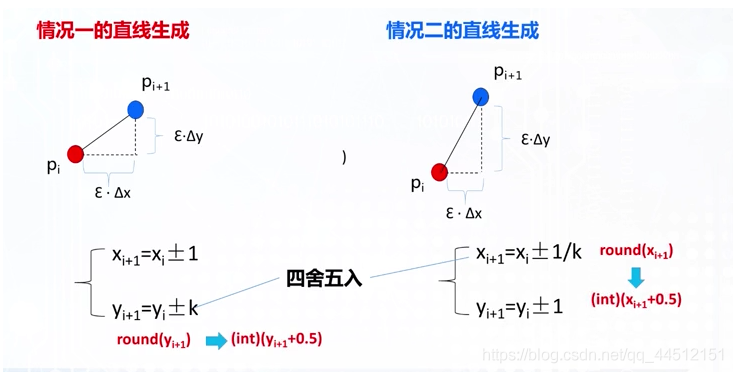
因为光栅化不能绘制半个像素点,所以求出的值需要进行四舍五入即加 0.5 后再进行取整。
DDA 算法是一个增量算法,它直观且容易实现,然而 x x x y y y y y y
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 void DrawLine_DDA (int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2int dx = x2 - x1;int dy = y2 - y1;int step = 0 ;if (Math.Abs(dy) > Math.Abs(dx)){else {float stepX = 1.0f * dx / step;float stepY = 1.0f * dy / step;int i = 0 ;float x = x1;float y = y1;int )x, (int )y);while ((i++)<step){int )x, (int )(y+0.5f ));
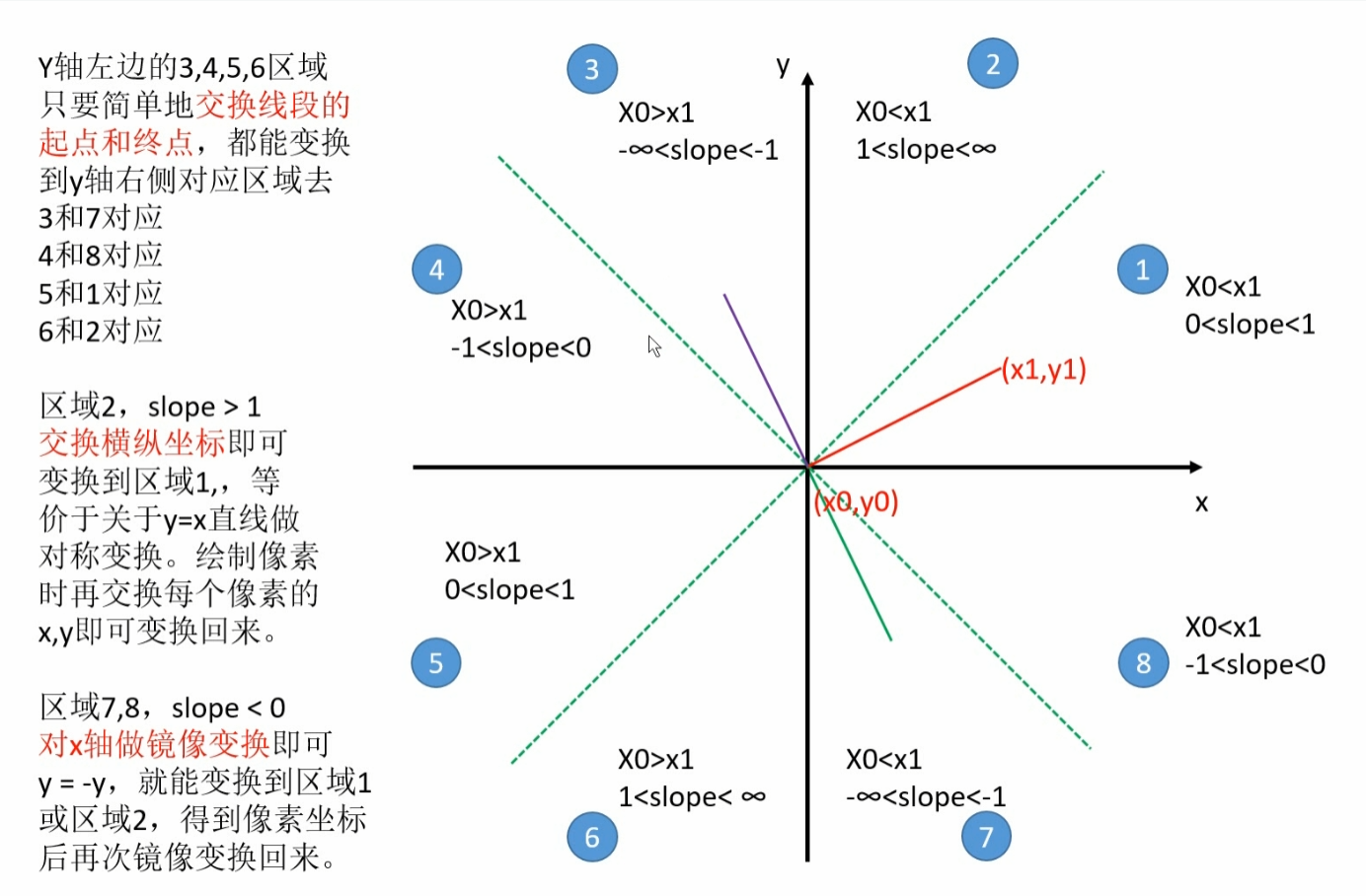
Bresenham画线
Bresenham 算法只用 int 类型的加减和比较来绘制直线,大大降低了需要的计算资源。
它的思路是:水平直线、竖直直线单独处理,剩余的部分等分为 8 个区域,然后从最简单的斜率大于 0 小于 1 的部分开始,剩下的 7 个部分稍作修改即可。
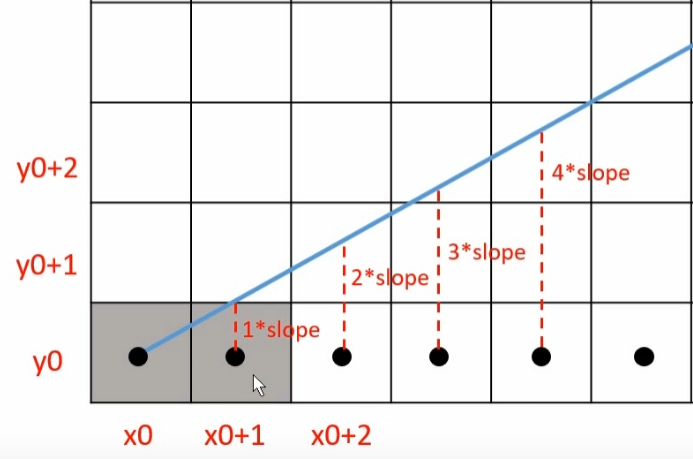
当斜率大于 0 小于 1 时,起始点为 (x 0 x_0 x 0 y 0 y_0 y 0 x 1 x_1 x 1 y 1 y_1 y 1 x 0 + i x_{0+i} x 0 + i y 0 + i × s l o p e y_0 + i \times slope y 0 + i × s l o p e y 0 + i × s l o p e + 0.5 y_0 + i \times slope + 0.5 y 0 + i × s l o p e + 0.5
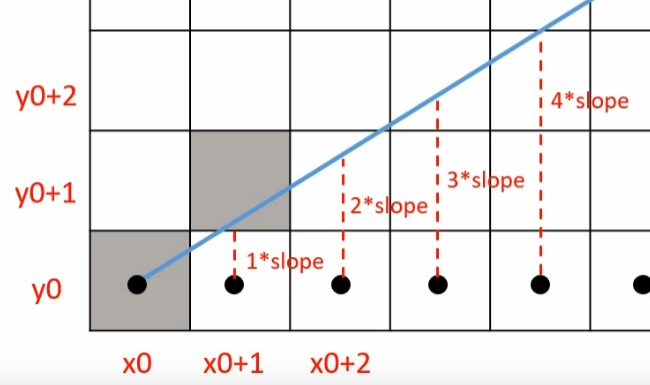
由于斜率大于 0 小于 1,相邻横坐标对应的纵坐标最多加 1。比如 x 0 + 1 x_{0+1} x 0 + 1 y 0 y_0 y 0 y 0 + 1 y_{0+1} y 0 + 1 y 0 + 2 y_{0+2} y 0 + 2
然而 Bresenham 算法是想避免 float 类型的运算和比较。以 x 0 + 1 x_{0+1} x 0 + 1
1 × s l o p e < 0.5 1 \times slope < 0.5 1 × s l o p e < 0.5 1 × s l o p e ≥ 0.5 1 \times slope \geq 0.5 1 × s l o p e ≥ 0.5 1 × s l o p e < 0.5 1 \times slope < 0.5 1 × s l o p e < 0.5 2 × s l o p e < 1 2 \times slope < 1 2 × s l o p e < 1 2 × Δ y < Δ x 2 \times \Delta y < \Delta x 2 × Δ y < Δ x 2 × Δ y − Δ x < 0 2 \times \Delta y - \Delta x < 0 2 × Δ y − Δ x < 0 Δ y = y 1 − y 0 , Δ x = x 1 − x 0 \Delta y = y_1 - y_0, \Delta x = x_1 - x_0 Δ y = y 1 − y 0 , Δ x = x 1 − x 0
若 2 × Δ y − Δ x < 0 2 \times \Delta y - \Delta x < 0 2 × Δ y − Δ x < 0 y ( x 0 + 1 ) = y 0 y(x_{0+1}) = y_0 y ( x 0 + 1 ) = y 0
否则 y ( x 0 + 1 ) = y 0 + 1 y(x_{0+1}) = y_{0+1} y ( x 0 + 1 ) = y 0 + 1
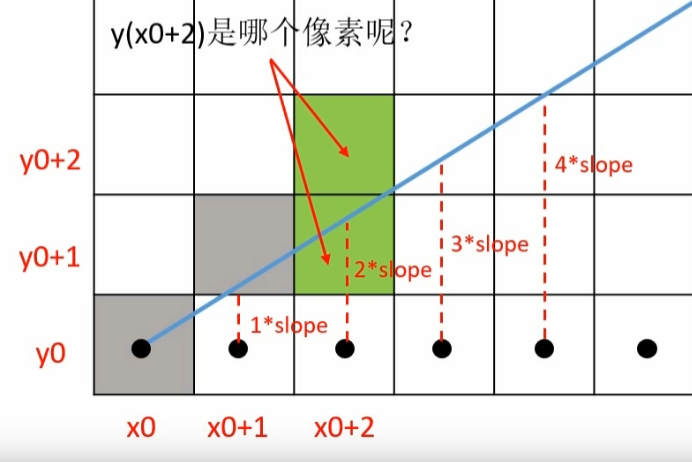
接着再考虑 x 0 + 2 x_{0+2} x 0 + 2
若前一个像素自右上方衍生出,需要比较 2 × s l o p e < 1.5 2 \times slope < 1.5 2 × s l o p e < 1.5 4 × Δ y − 3 × Δ x < 0 4 \times \Delta y - 3 \times \Delta x < 0 4 × Δ y − 3 × Δ x < 0 4 × Δ y − 3 × Δ x = 2 × Δ y − Δ x + ( 2 × Δ y − 2 × Δ x ) 4 \times \Delta y - 3 \times \Delta x = 2 \times \Delta y - \Delta x + (2 \times \Delta y - 2 \times \Delta x) 4 × Δ y − 3 × Δ x = 2 × Δ y − Δ x + ( 2 × Δ y − 2 × Δ x )
若前一个像素自右方衍生出,需要比较 2 × s l o p e < 0.5 2 \times slope < 0.5 2 × s l o p e < 0.5 4 × Δ y − Δ x < 0 4 \times \Delta y - \Delta x < 0 4 × Δ y − Δ x < 0 4 × Δ y − Δ x = 2 × Δ y − Δ x + ( 2 × Δ y ) 4 \times \Delta y - \Delta x = 2 \times \Delta y - \Delta x + (2 \times \Delta y) 4 × Δ y − Δ x = 2 × Δ y − Δ x + ( 2 × Δ y )
同样的思路可以一直推下去直到线段的末尾。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 public void DrawLine_Bresenham (int x0, int x1, int y0, int y1bool steep = false ;if (Math.Abs(x0 - x1) < Math.Abs(y0 - y1))ref x0, ref y0);ref x1, ref y1);true ;if (x0 > x1)ref x0, ref x1);ref y0, ref y1);int dx = x1 - x0;int dy = y1 - y0;int derror = Math.Abs(dy) * 2 ;int error = 0 ;int y = y0;for (int x = x0; x <= x1; x++)if (steep)else if (error > dx)1 : -1 );2 ;
中点画线
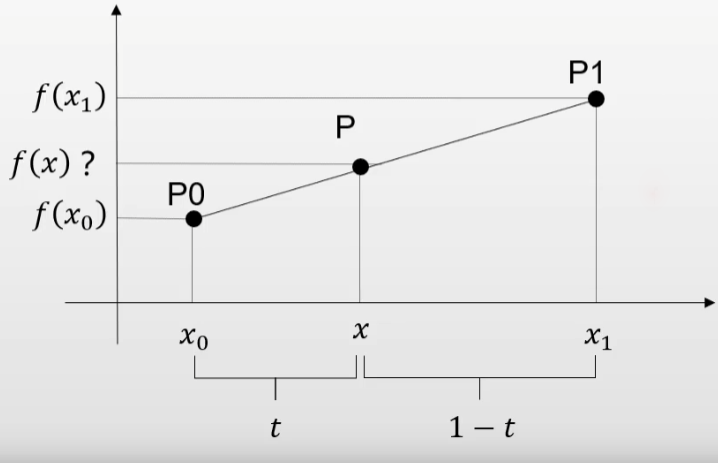
如下图
其中,
P = p 0 + ( P 1 − P 0 ) t = P 0 − t P 0 + t P 1 = ( 1 − t ) P 0 + t P 1 \begin{aligned}
P &= p_0 + (P_1 - P_0)t\\
&= P_0 - tP_0 + tP_1\\
&= (1 - t)P_0 + tP_1
\end{aligned}
P = p 0 + ( P 1 − P 0 ) t = P 0 − t P 0 + t P 1 = ( 1 − t ) P 0 + t P 1
那么
f ( x ) = ( 1 − t ) × f ( x 0 ) + t × f ( x 1 ) f(x) = (1 - t) \times f(x_0) + t \times f(x_1)
f ( x ) = ( 1 − t ) × f ( x 0 ) + t × f ( x 1 )
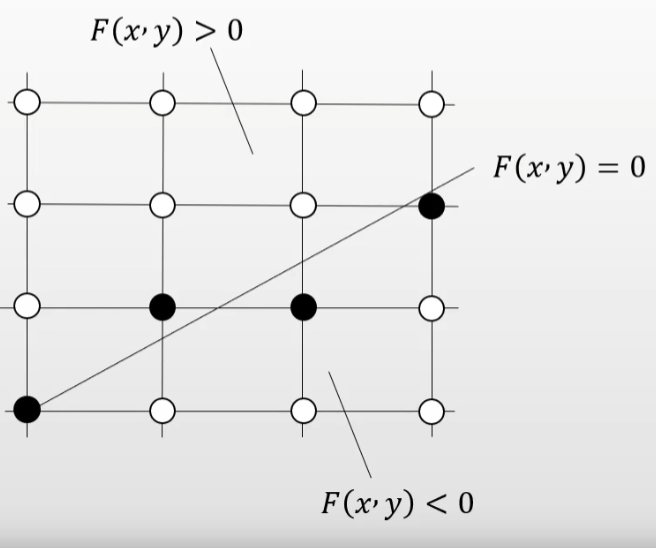
直线隐函数方程为:
F ( x , y ) = y − k x − b = 0 F(x, y) = y - kx - b = 0
F ( x , y ) = y − k x − b = 0
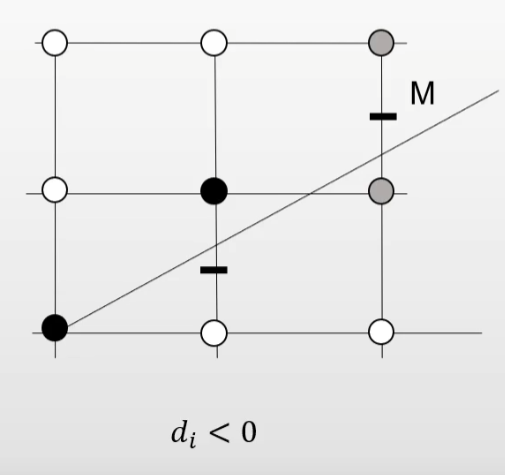
假设已经确定了要显示的点 (x i x_i x i y i y_i y i
d i = F ( x i + 1 , y i + 0.5 ) = y i + 0.5 − k ( x i + 1 ) − b d_i = F(x_i + 1, y_i + 0.5) = y_i + 0.5 - k(x_i + 1) - b
d i = F ( x i + 1 , y i + 0.5 ) = y i + 0.5 − k ( x i + 1 ) − b
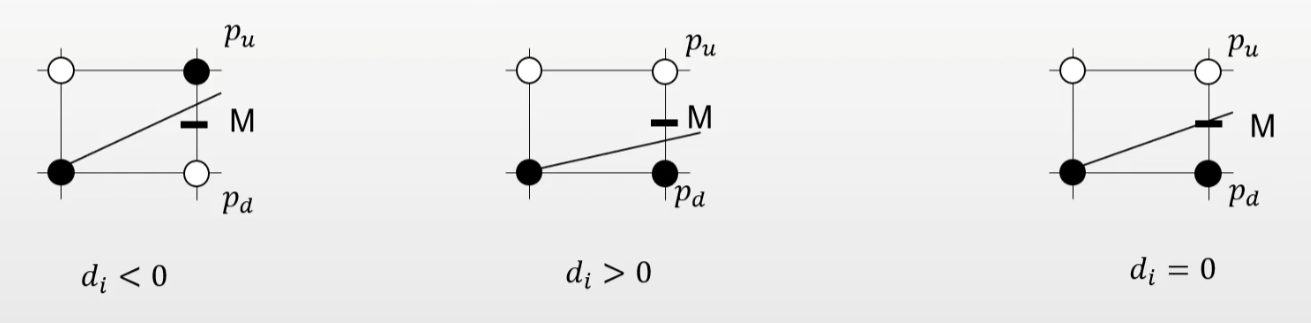
y i + 1 = { y i + 1 , ( d i < 0 ) y i , ( d i ≥ 0 ) y_{i+1} = \begin{cases}
y_i + 1, (d_i < 0)\\
y_i,\quad(d_i \geq 0)
\end{cases}
y i + 1 = { y i + 1 , ( d i < 0 ) y i , ( d i ≥ 0 )
当 d i < 0 d_i < 0 d i < 0
d i + 1 = F ( x i + 2 , y i + 1.5 ) = y i + 1.5 − k ( x i + 2 ) − b = y i + 0.5 − k ( x i + 1 ) − b + 1 − k = d i + 1 − k \begin{aligned}
d_{i+1} &= F(x_i + 2, y_i + 1.5)\\
&= y_i + 1.5 - k(x_i + 2) - b\\
&= y_i + 0.5 - k(x_i + 1) - b + 1 - k\\
&= d_i + 1 - k
\end{aligned}
d i + 1 = F ( x i + 2 , y i + 1.5 ) = y i + 1.5 − k ( x i + 2 ) − b = y i + 0.5 − k ( x i + 1 ) − b + 1 − k = d i + 1 − k
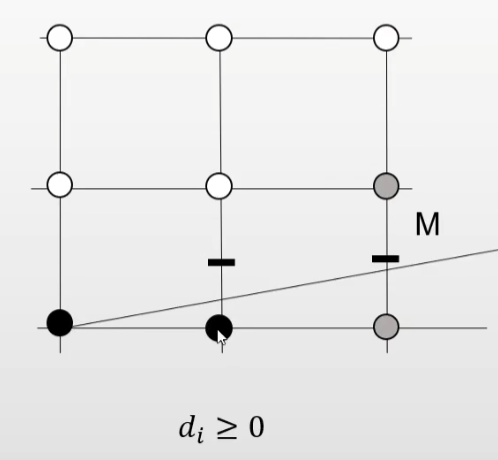
当 d i ≥ 0 d_i \geq 0 d i ≥ 0
d i + 1 = F ( x i + 2 , y i + 0.5 ) = y i + 0.5 − k ( x i + 2 ) − b = y i + 0.5 − k ( x i + 1 ) − b − k = d i − k \begin{aligned}
d_{i+1} &= F(x_i + 2, y_i + 0.5)\\
&= y_i + 0.5 - k(x_i + 2) - b\\
&= y_i + 0.5 - k(x_i + 1) - b - k\\
&= d_i - k
\end{aligned}
d i + 1 = F ( x i + 2 , y i + 0.5 ) = y i + 0.5 − k ( x i + 2 ) − b = y i + 0.5 − k ( x i + 1 ) − b − k = d i − k
当 d i < 0 d_i < 0 d i < 0 d i + 1 = d i + 1 − k d_{i+1} = d_i + 1 - k d i + 1 = d i + 1 − k d i ≥ 0 d_i \geq 0 d i ≥ 0 d i + 1 = d i − k d_{i+1} = d_i - k d i + 1 = d i − k
中点误差项初始值为:
d 0 = F ( x 0 + 1 , y 0 + 0.5 ) = y 0 + 0.5 − k ( x 0 + 1 ) − b = y 0 − k x − b − k + 0.5 = 0.5 − k \begin{aligned}
d_0 &= F(x_0 + 1, y_0 + 0.5)\\
&= y_0 + 0.5 - k(x_0 + 1) - b\\
&= y_0 - kx - b - k + 0.5\\
&= 0.5 - k
\end{aligned}
d 0 = F ( x 0 + 1 , y 0 + 0.5 ) = y 0 + 0.5 − k ( x 0 + 1 ) − b = y 0 − k x − b − k + 0.5 = 0.5 − k
接下来,我们需要进行整数化处理:
令 d d d 2 Δ x 2\Delta x 2Δ x e e e y y y
e = 2 d Δ x e = 2d\Delta x
e = 2 d Δ x
此时误差项初始值为:
e 0 = 2 d 0 Δ x = 2 ( 0.5 − k ) Δ x = Δ x − 2 Δ y e_0 = 2d_0\Delta x = 2(0.5 - k)\Delta x = \Delta x - 2\Delta y
e 0 = 2 d 0 Δ x = 2 ( 0.5 − k ) Δ x = Δ x − 2Δ y
此时误差项的递推公式为:
e < 0 , e = 2 ( d + 1 − k ) Δ x = 2 d Δ x + 2 Δ x − 2 k Δ x = e + 2 Δ x − 2 Δ y e ≥ 0 , e = 2 ( d − k ) Δ x = 2 d Δ x − 2 k Δ x = e − 2 Δ y \begin{aligned}
e < 0, e &= 2(d + 1 - k)\Delta x = 2d\Delta x + 2\Delta x - 2k\Delta x = e + 2\Delta x - 2\Delta y\\
e \geq 0, e &= 2(d - k)\Delta x = 2d\Delta x - 2k\Delta x = e - 2\Delta y
\end{aligned}
e < 0 , e e ≥ 0 , e = 2 ( d + 1 − k ) Δ x = 2 d Δ x + 2Δ x − 2 k Δ x = e + 2Δ x − 2Δ y = 2 ( d − k ) Δ x = 2 d Δ x − 2 k Δ x = e − 2Δ y
e i + 1 = { e i + 2 Δ x − 2 Δ y , ( e < 0 ) e i − 2 Δ y , ( e ≥ 0 ) e_{i+1} = \begin{cases}
e_i + 2\Delta x - 2\Delta y, (e < 0)\\
e_i - 2\Delta y,\quad(e \geq 0)
\end{cases}
e i + 1 = { e i + 2Δ x − 2Δ y , ( e < 0 ) e i − 2Δ y , ( e ≥ 0 )
那么此时进行画线操作,从 P 0 P_0 P 0 P 1 P_1 P 1 x x x e e e x x x y y y e < 0 e < 0 e < 0 x + 1 x+1 x + 1 y + 1 y+1 y + 1 e = e + 2 Δ x − 2 Δ y e = e + 2\Delta x - 2\Delta y e = e + 2Δ x − 2Δ y x + 1 x+1 x + 1 y y y e = e − 2 Δ y e = e - 2\Delta y e = e − 2Δ y
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 void DrawLine_MidPoint (int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1bool bInterchange = false ;int dx = abs(x1 - x0);int dy = abs(y1 - y0);int signx = x0 < x1 ? 1 : -1 ;int signy = y0 < y1 ? 1 : -1 ;if (dy > dx){int temp = dy;true ;int e = dx - 2 * dy;int x = x0;int y = y0;for (int i = 1 ; i <= dx; i++){if (bInterchange){else {if (e < 0 ){if (bInterchange){else {2 * dx - 2 * dy;else {2 * dy;
画三角形方法
利用线性插值画三角形
让我们假设三角形的三个点 t0,t1, t2,通过 y 坐标的大小排序成升序。 那么,边界 A 在是 t0 和 t2 之间的线段,边界 B 是 t0 和 t1 之间线段,最后的在 t1 和 t2 之间的线段。以高度差作为循环控制变量,从左到右对相同高度的像素进行着色。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 void DrawTriangle1 (Point t0, Point t1, Point t2 )if (t0.y == t1.y && t1.y == t2.y) return ;if (t0.y > t1.y)ref t0, ref t1);if (t0.y > t2.y)ref t0, ref t2);if (t1.y > t2.y)ref t1, ref t2);int total_height = t2.y - t0.y;for (int i = 0 ; i < total_height; i++)bool second_half = i > t1.y - t0.y || t1.y == t0.y;int segment_height = second_half ? t2.y - t1.y : t1.y - t0.y;float alpha = (float )i / total_height;float beta = (float )(i - (second_half ? t1.y - t0.y : 0 )) / segment_height;beta if (A.x > B.x ) ref A, ref B);for (int j = A.x; j <= B.x; j++)float phi = B.x == A.x ? 1f : (float )(j - A.x) / (float )(B.x - A.x);
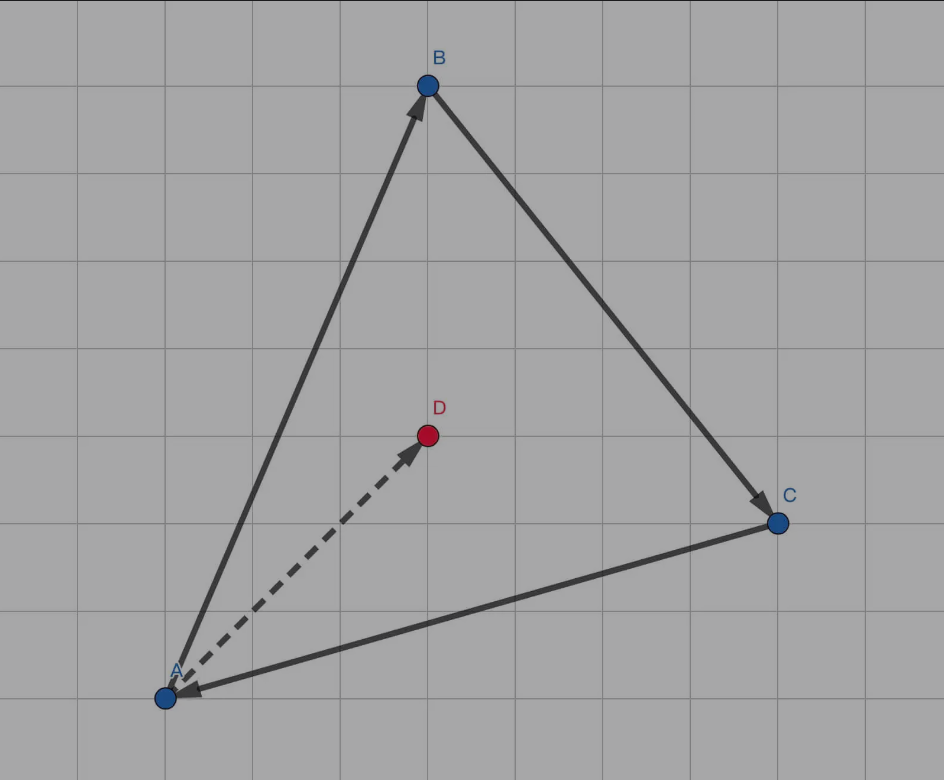
利用叉乘画三角形
对于三角形 △ A B C \triangle ABC △ A BC A B ⟶ \overset{\longrightarrow}{AB} A B ⟶ B C ⟶ \overset{\longrightarrow}{BC} BC ⟶ C A ⟶ \overset{\longrightarrow}{CA} C A ⟶ P P P
对二维向量叉乘做一个定义:
假设有两个二维向量 a ⃗ \vec{a} a b ⃗ \vec{b} b z z z a ⃗ \vec{a} a b ⃗ \vec{b} b c ⃗ \vec{c} c c ⃗ \vec{c} c x x x y y y z z z a . x × b . y − b . x × a . y a.x \times b.y - b.x \times a.y a . x × b . y − b . x × a . y c ⃗ \vec{c} c z z z
如果 z z z b ⃗ \vec{b} b a ⃗ \vec{a} a
如果 z z z b ⃗ \vec{b} b a ⃗ \vec{a} a
如果 z z z b ⃗ \vec{b} b a ⃗ \vec{a} a
A B ⟶ × A P ⟶ \overset{\longrightarrow}{AB} \times \overset{\longrightarrow}{AP} A B ⟶ × A P ⟶ P P P A B AB A B B C ⟶ × B P ⟶ \overset{\longrightarrow}{BC} \times \overset{\longrightarrow}{BP} BC ⟶ × BP ⟶ P P P B C BC BC C A ⟶ × C P ⟶ \overset{\longrightarrow}{CA} \times \overset{\longrightarrow}{CP} C A ⟶ × CP ⟶ P P P A C AC A C
综合以上三个条件,我们可以判断 P P P △ A B C \triangle ABC △ A BC P P P △ A B C \triangle ABC △ A BC P P P △ A B C \triangle ABC △ A BC
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 Vector3 crossProduct (Point[] points, Point P ) new Vector2(points[1 ].x - points[0 ].x, points[1 ].y - points[0 ].y);new Vector2(points[2 ].x - points[1 ].x, points[2 ].y - points[1 ].y);new Vector2(points[0 ].x - points[2 ].x, points[0 ].y - points[2 ].y);new Vector2(P.x - points[0 ].x, P.y - points[0 ].y);new Vector2(P.x - points[1 ].x, P.y - points[0 ].y);new Vector2(P.x - points[2 ].x, P.y - points[0 ].y);return new Vector3(AB.x * AP.y - AP.x * AB.y, BC.x * BP.y - BP.x * BC.y, CA.x * CP.y - CP.x * CA.y);void DrawTriangle2 (Point[] points )new Vector2(float .MaxValue,float .MaxValue);new Vector2(float .MinValue,float .MinValue);new Vector2(canvas.Width - 1 , canvas.Height - 1 );for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++)0f , Math.Min(bboxmin.x, points[i].x));0f , Math.Min(bboxmin.y, points[i].y));for (p.x = (int )Math.Ceiling(bboxmin.x); p.x <= (int )Math.Floor(bboxmax.x); p.x++){for (p.y = (int )Math.Ceiling(bboxmin.y); p.y <= (int )Math.Floor(bboxmax.y); p.y++){if (cross.x < 0 || cross.y < 0 || cross.z < 0 )continue ;
利用三角形重心画三角形
有关于三角形重心的介绍可以参考上一篇博文,下面给出代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 public Vector3 CrossProduct (Vector3 v1, Vector3 v2 )return new Vector3(public Vector3 Barycentric (Point A, Point B, Point C, Point P )new Vector3(B.x - A.x, C.x - A.x, A.x - P.x);new Vector3(B.y - A.y, C.y - A.y, A.y - P.y);if (Math.Abs(u.z) > float .Epsilon)return new Vector3(1f - (u.x + u.y) / u.z, u.y / u.z, u.x / u.z);return new Vector3(-1 , 1 , 1 );void DrawTriangle3 (Point[] points )new Vector2(float .MaxValue,float .MaxValue);new Vector2(float .MinValue,float .MinValue);new Vector2(canvas.Width - 1 , canvas.Height - 1 );for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++)0f , Math.Min(bboxmin.x, points[i].x));0f , Math.Min(bboxmin.y, points[i].y));for (p.x = (int )Math.Ceiling(bboxmin.x); p.x <= (int )Math.Floor(bboxmax.x); p.x++)for (p.y = (int )Math.Ceiling(bboxmin.y); p.y <= (int )Math.Floor(bboxmax.y); p.y++)0 ], points[1 ], points[2 ], p);if (bc_screen.x < 0f || bc_screen.y < 0f || bc_screen.z < 0f ) continue ;